MyoSleeve
MyoSleeve is a wearable device with an adaptable sleeve that uses high-density surface electromyography (HD-sEMG) sensors connected to a wireless portable biopotential amplifier capable of recording up to 256 EMG signals. The innovative technology of HD-sEMG by MyoSleeve will be employed for muscle assessment during rehabilitation exercises. MyoSleeve provides a reliable quantitative estimate of muscular imbalance, co-activation, and fatigue.
Technology Description
MyoSleeve is a wearable device with an adaptable sleeve that uses high-density surface electromyography (HD-sEMG) sensors connected to a wireless portable biopotential amplifier capable of recording up to 256 EMG signals. The innovative technology of HD-sEMG by MyoSleeve will be employed for muscle assessment during rehabilitation exercises. MyoSleeve provides a reliable quantitative estimate of muscular imbalance, co-activation, and fatigue.
Unmet Clinical Problem
The standard motor rehabilitation procedure and its evaluation are mainly based on functional exercises, strength production, and movement imbalance assessment. Surprisingly, activity at the neuromuscular level is not assessed even if it is the source of the disorder, and therapists have only the patient's opinion about muscular fatigue or pain. Despite being crucial to define the rehabilitation program and its progress, patients, and therapists are unaware of the muscular condition because there is still no commercial device that can adequately assess it.
Epicondylitis, also known as tennis elbow, is a clinical condition caused by tendon inflammation due to the overuse of the muscles attached to your elbow, which are required to straighten your wrist. Tiny tears and inflammation may form close to the bony lump (the lateral epicondyle) outside the elbow if the muscles are overworked. Intramuscular electromyography (EMG) is commonly used in clinical practice to assess muscle function for accurate diagnosis. Although the information obtained by intramuscular electromyography, which is based on needle electrodes, has the potential to be extremely beneficial, its use in routine rehabilitation sessions is not indicated because it causes the patient some discomfort and pain.
The non-invasive alternative is surface EMG, which is based primarily on a pair of electrodes. Commercial HD-sEMG devices are not used often. They are not practical and easy to use because they are not wearable or big, consume a lot of power, and are used in combination with conductive gel, which requires a long preparation time.
Surface EMG is a non-invasive option that relies primarily on several electrodes. There aren't many commercial HD-sEMG devices in use. In addition, they are not wearable, they use a lot of power, and they must be combined with conductive gel, making the overall process lengthy and impractical.
Proposed Solution
MyoSleeve is a medical device with a technology that integrates High Sensity Surface Electromyogram sensors (HD-sEMG) and low-consumption electronic amplifiers into a standard long-sleeve or T-shirt to produce a wearable, wireless, and easy-to-use HD-sEMG device.
MyoSleeve offers a solution that benefits patients and physicians by providing a reliable quantitative assessment of muscular imbalance, coactivation, and fatigue that helps improve the overall rehabilitation process.
- MyoSleeve contributes to patients’ welfare and rehabilitation experience due to its adaptable, smart textile sleeve without using conductive gel or needles to record neuromuscular data.
- MyoSleeve benefits the physician by delivering information about the neuromuscular activity and spatial distribution related to movement duration and fatigue, joint angle, and level of contraction.
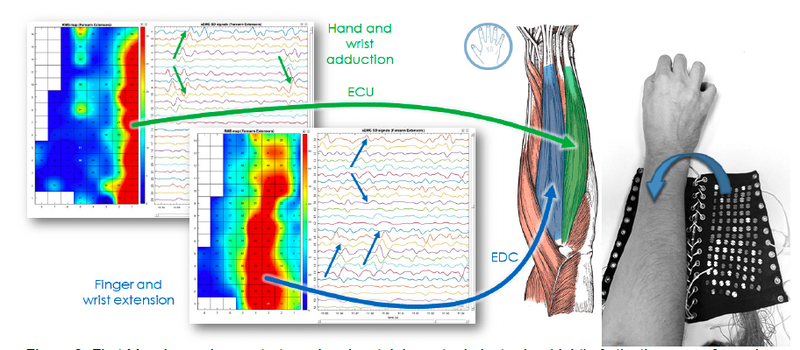
“HD-sEMG is the only EMG technique that estimates the spatial distribution of motor units within a muscle.”
By observing the amplitude or intensity of the signals recorded by each channel, it is possible to analyze how different muscle regions are activated depending on the angle of the joint, the level of contraction, the duration of movement, and the fatigue.
The information that can be extracted from all of them using HD-sEMG is of great interest during the rehabilitation process and also after continuing the prevention exercises and what is, among others:
- Extraction of the muscle coactivation pattern
HD-sEMG can monitor the spatial activation of individual muscles, muscle groups, or even different muscle parts. With this information, you can know which muscles are activated during different movements or phases of a movement. This combination of activation of different muscles is called a coactivation pattern.
- Monitoring of action potentials (MUAPs).
Multichannel records allow the identification of different MUAPs while observing their spread along muscle fibers. One can count the number of active motor units but also estimate the propagation speed of these.
- Estimation of muscle fatigue
Muscle fatigue is a decrease in muscle tension as a result of the previous contractile activity. Fatigue changes the characteristics of the myoelectric signals. One of the primary manifestations is the decrease in the conduction velocity of the muscle fibers, which can be observed while monitoring the propagation of the MUAPs. Fatigue also causes synchronization of the activations, which, in addition to the decrease in conduction velocity, shifts the energy spectrum to lower frequencies and increases the amplitude of the EMG signal. These measures can be used to detect the presence of muscle fatigue and warn the patient not to continue exercising the muscle.
MyoSleeve, in contrast to currently available medical devices for rehabilitation, analyzes high-precision muscular data in real time and guides the patient through them, providing the physiotherapist with a detailed evaluation of muscle injury and the patient's progress. In addition, MyoSleeve will allow clinicians to customize patients' rehabilitation protocols, ensuring proper execution of exercises and speeding up patient recovery by increasing treatment adherence.
Share: